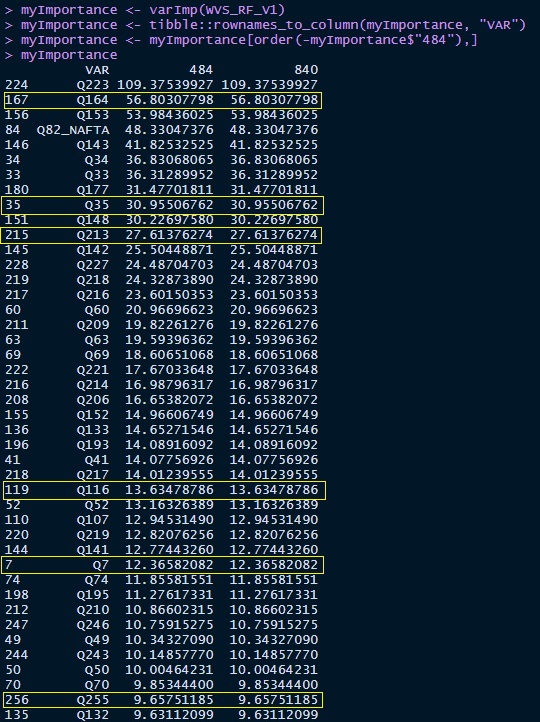
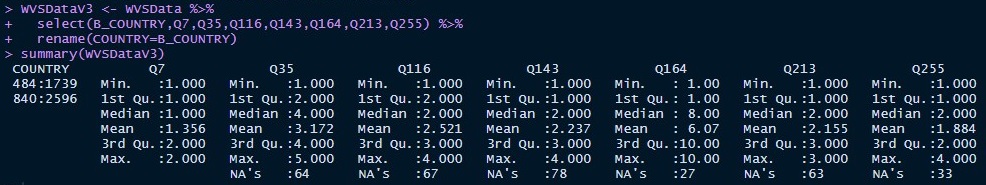
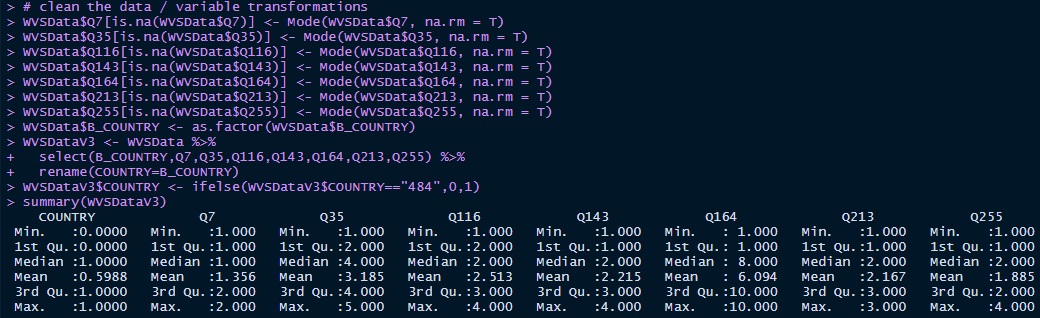
Afterwards I plotted the variables by country to compare the distributions:
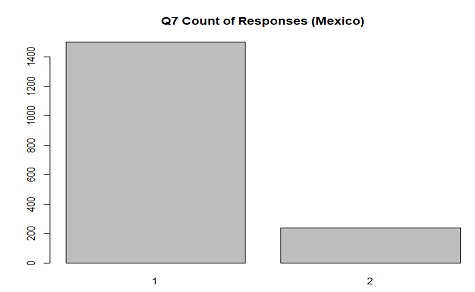
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q7(child manners) where 1 is "Mentioned" and 2 is "Not mentioned"
With the importance of family and being a good host in Mexican culture this distribution makes sense.
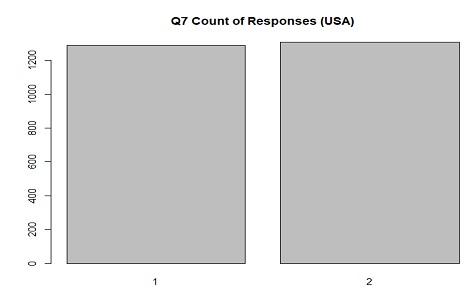
The distribution of responses in USA for Q7(child manners) where 1 is "Mentioned" and 2 is "Not mentioned"
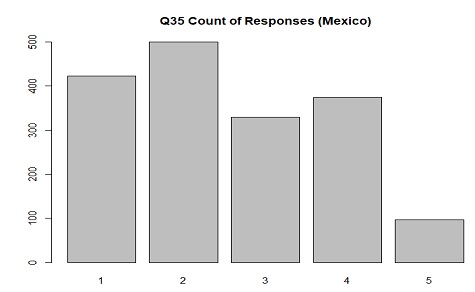
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q35(high earning wife) where 1 is "Agree strongly" and 5 is
"Disagree strongly"
With strong traditional gender roles in Mexican families this distribution makes sense.
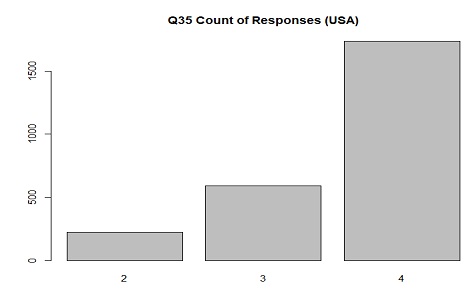
The distribution of responses in USA for Q35(high earning wife) where 1 is "Agree strongly" and 5 is
"Disagree strongly"
With weaker traditional gender roles in US families this distribution makes sense. Its interesting
that none of the respondents agreed or disagreed strongly.
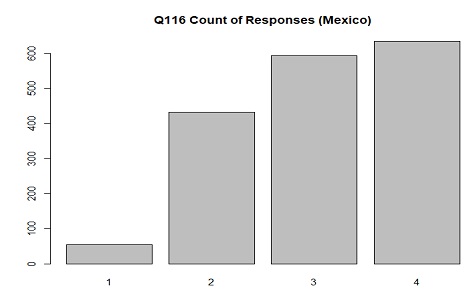
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q116(civil service providers are corrupt) where 1 is
"None of them" and 4 is "All of them"
With the distrust in government overall in Mexico this distribution makes sense.
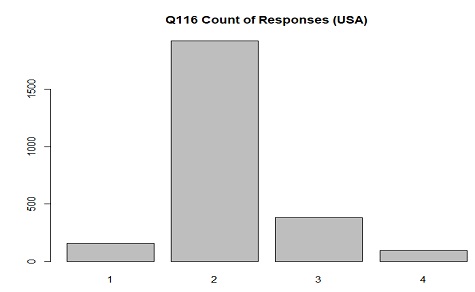
The distribution of responses in USA for Q116(civil service providers are corrupt) where 1 is
"None of them" and 4 is "All of them"
With US citizens having high trust in goverment overall this distribution makes sense.
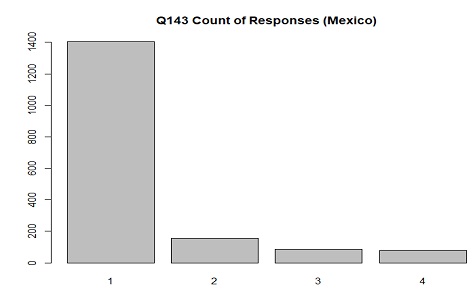
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q143(worry about children's education) where 1 is "Very much" and
4 is "Not at all"
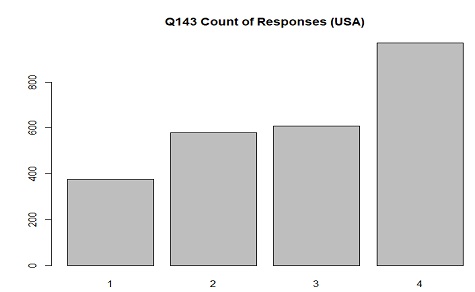
The distribution of responses in USA for Q143(worry about children's education) where 1 is "Very much" and
4 is "Not at all"
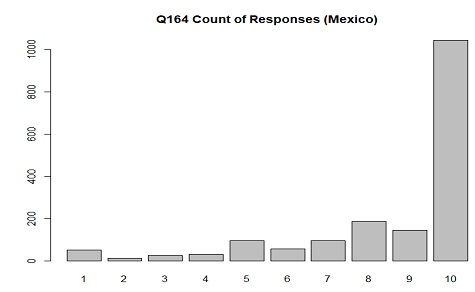
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q164(importance of god) where 1 is "Not at all important" and 10 is "Very important"
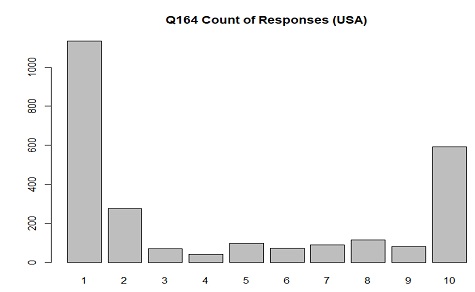
The distribution of responses in USA for Q164(importance of god) where 1 is "Not at all important" and 10 is "Very important"
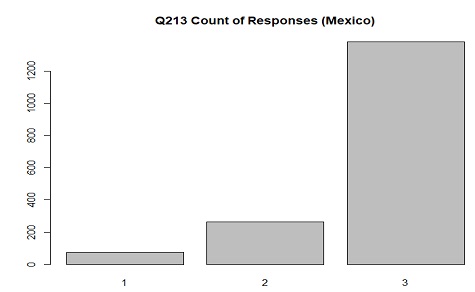
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q213(action/activism through donating) where 1 is "Have done", 2 is "Might do",
and 3 is "Would never do"
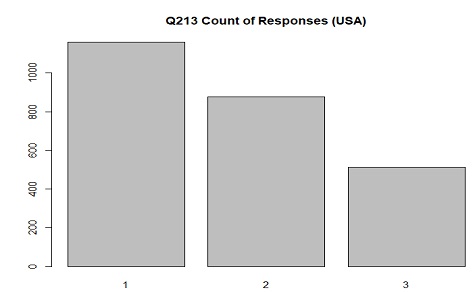
The distribution of responses in USA for Q213(action/activism through donating) where 1 is "Have done", 2 is "Might do",
and 3 is "Would never do"
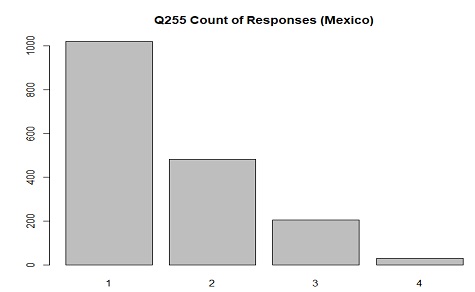
The distribution of responses in Mexico for Q255(closeness to village/town/city) where 1 is "Very close" and 4 is "Not close at all"
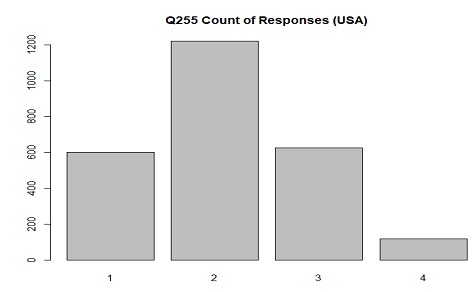
The distribution of responses in USA for Q255(closeness to village/town/city) where 1 is "Very close" and 4 is "Not close at all"
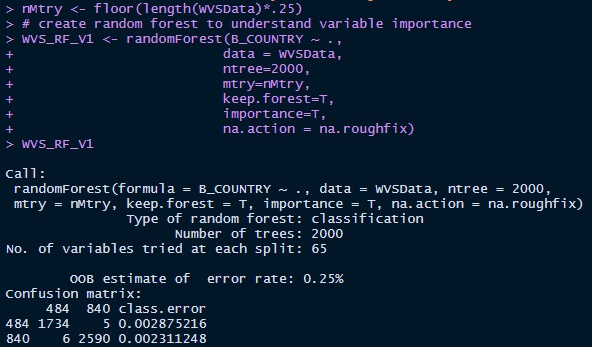
Logistic Regression Model
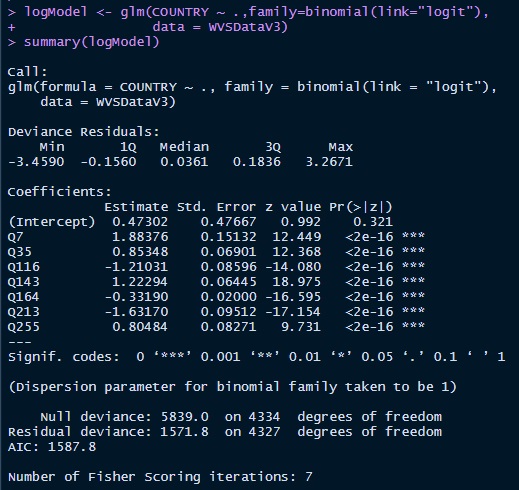
The summary below allows us to make an initial check of the model.
The first column we look at is the z value.
The further from 0 a value is, the stronger the variable is as a predictor.
In this case, we can see Q143(worry about children’s education) is the strongest predictor.
We also see that Q255(closeness to village/town/city) is our weakest predictor.
Looking at the p-value for all variables we see none are greater than 0.05 i.e. they are statistically significant.
Accuracy of Model
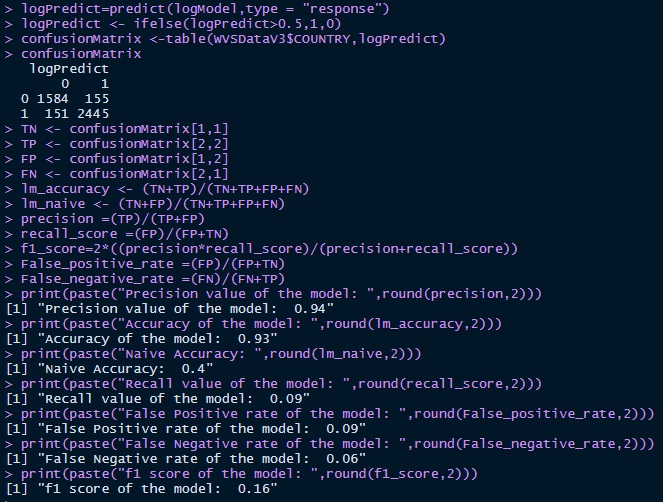
Finally we want to evaulate the accuracy of the model.
For this we look at the accuracy of the model compared to the naive model.
Additionally, we look at recall, false positive rate, false negative rate and the f1 score.
We can see that this model far outperforms the naive model with an accuracy of 93% compared to 40%
Repeat in KNIME
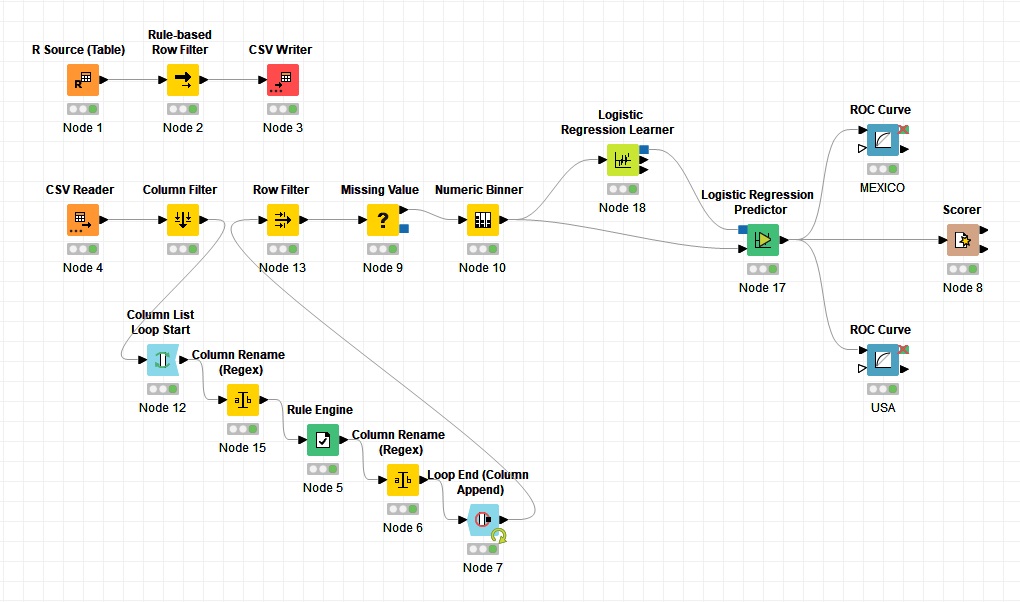
To demonstrate understanding of the concepts and adaptability, we were tasked with also creating the model in KNIME.
Because I am more comfortable in R and due to time constraints I did not recreate the random forest in KNIME to
determine variable importance, instead I just used the variables selected in R.
In KNIME I used the R Source node to load the spss file.
Then I narrow the dataset down to Mexico and US respondents with a row filter.
Then I saved the file as a CSV to ease of use in the KNIME model.
Using the scorer node we see that our model is producing a similar accuracy:

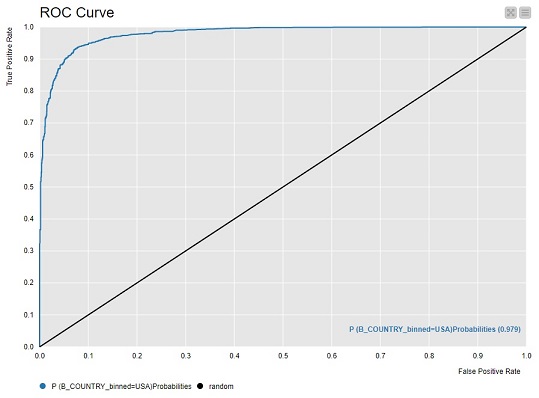
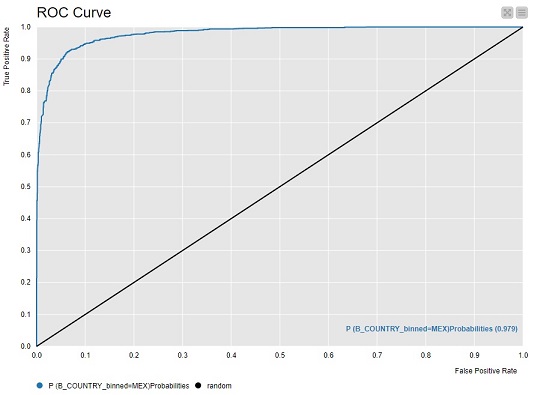
ROC Curves
Due to deadline constraints and ease of use I only created the ROC curves in KNIME.
In the future I would like to add the code to plot the ROC curves in R.
ROC Curve for Mexico:
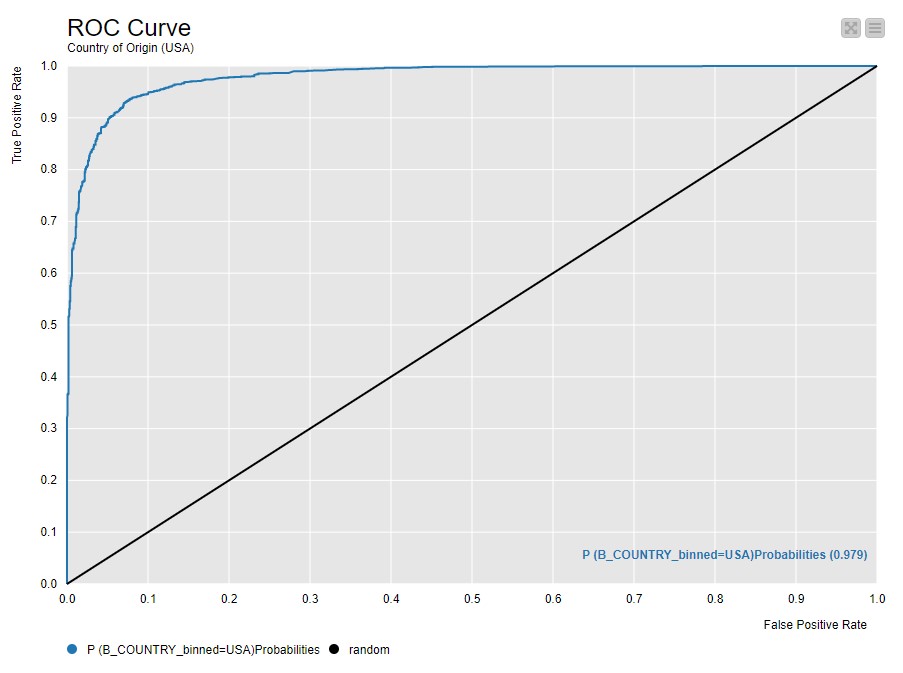
ROC Curve for USA: